If you are new to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain, you may have heard the term “Proof of Stake (PoS),” which is an alternative to Proof of Work (PoW). These 2 concepts are known as consensus mechanisms and are essential for cryptocurrencies’ securities and transactions.
Quantum Mechanic suggested Proof of Stake; later, the pseudonyms are Sunny King, and Scott Nadal created Proof of Stake, which is currently used by cryptocurrencies like Solana, Terra, Cardano, etc.
Let us explain more about Proof of Stake –
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus method that processes transactions and creates new blocks in the blockchain. A consensus method validates entries in the distributed database by providing security to the database. In cryptocurrency, the database is known as a blockchain; thus, the consensus method provides security to the blockchain.
Understanding the mechanism of Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake (PoS) reduces the complex computational problem-solving work which is required for transactions and blocks. Thus, Proof of Stake (PoS) increases the security of the blockchain network.
The verification under the Proof of Stake (PoS) is done through the users holding native tokens. Those users offer their tokens to get the chance to validate the blocks. The users who have staked their native tokens can become “Validators.”
Validators are selected randomly to validate the block under the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism, but the competitive-based mechanism is used under the Proof of Work (PoW).
There is a requirement that the user needs to complete to become a validator like if we go with Ethereum, the user needs 32 ETH to be staked in the blockchain before becoming a validator.
Blocks are verified with numerous validators, but when one validator verifies that the block is accurate, the block is finalized and closed further.
Different Proof of Stake (PoS) will use different methods for verifying the blocks. Ethereum will use shards for transactions when it is transitioned from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS).
Here, a validator will verify the transaction by adding it to the shard block, where 128 validators will attest to the shard block. Once the shards are validated, and blocks have been created, 2/3rd of the validators must agree that the transaction in the shard block is valid, and then the block is closed.
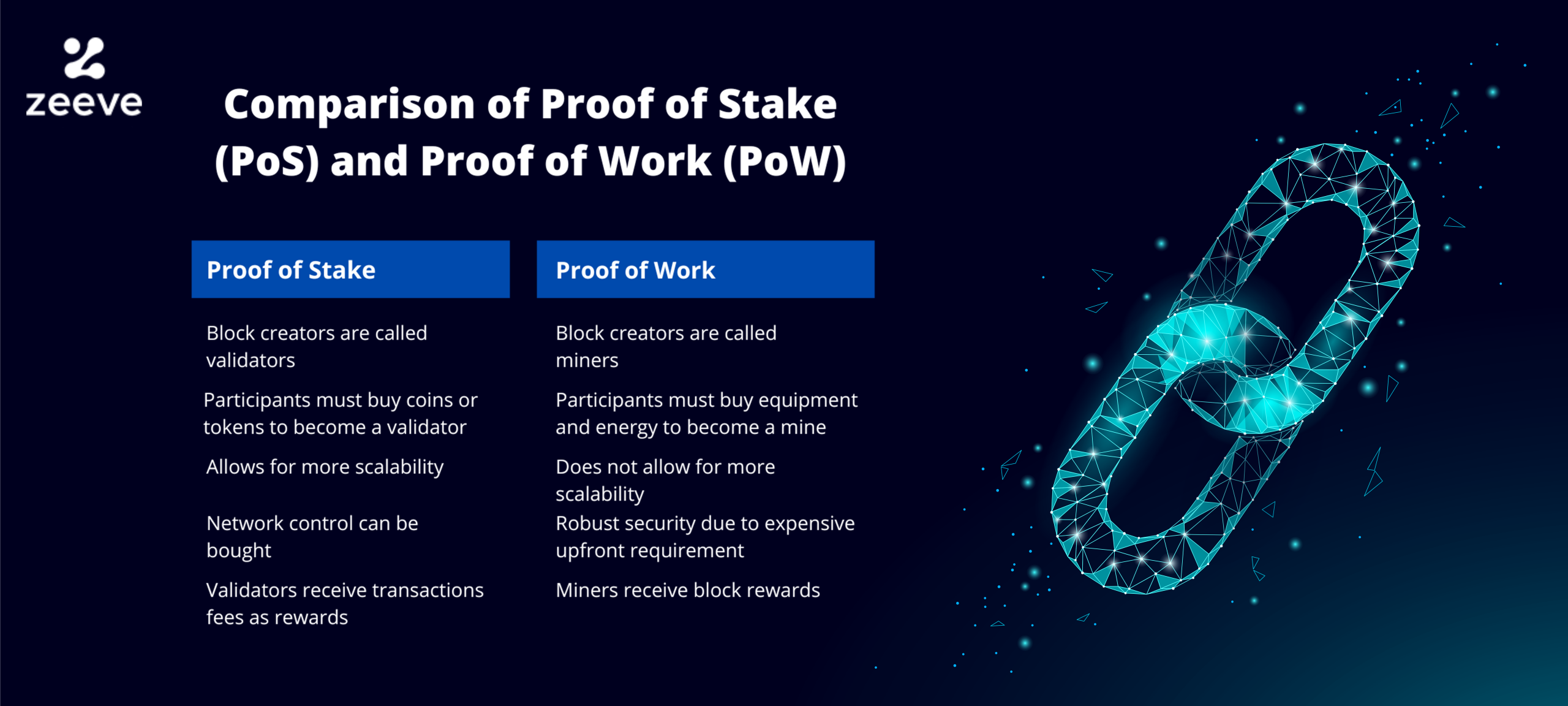
Difference between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS)
Both PoW and PoS consensus methods have different approaches; thus, they help blockchain by validating information, synchronizing data, and processing transactions. Although both consensus methods can maintain the blockchain, they come with their pros and cons. Let us explain it below –
| Number | Details | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| 1 | Block Creators | Block creators are called Miners | Block creators are called Validators |
| 2 | Requirements | Users must buy equipment and significant energy to become Miners. | Users must purchase tokens or coins to become Validators. |
| 3 | Scalability | It does not allow scalability. | It allows scalability. |
| 4 | Environment Friendly | Not environmentally friendly. | It is environmentally friendly. |
| 5 | Rewards | Miners receive block rewards. | Validators receive transaction fees and rewards. |
Variants of Proof of Stake (PoS)
1- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Daniel Larimer founded Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), a consensus algorithm, in 2014. Some cryptocurrency projects like BitShares, Steem, Ark, and Lisk use Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
An election system is used in Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) to select nodes to verify blocks. Those nodes are called “Block Producers” or “Witnesses.” In DPos System, the user can direct vote or can provide voting power to another entity on his behalf. Due to the low entry threshold, DPos is more decentralized.
2- Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS)
Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS) was launched in 2017, and the consensus algorithm was developed to solve various difficulties which were related to Proof of Stake (PoS) and its variant – Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
The LPoS system works the same as Proof of Stake (PoS), but it uses leasing to provide nodes with small stakes and provides incentives to be part of the consensus.
The LPoS system is used in the WAVES blockchain platform, and here, the leaser should hold 1,000 WAVES to participate in generating blocks. If enough coin holders wish to lease their coin, the node balance can be empty; thus, it requires 1000 WAVES to produce a block. Once the node is selected for block production, the leaser will receive a percentage fee received by the node.
3- Hybrid Proof of Stake (HPoS)
Hybrid Proof of Stake is the combined version of the Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW). The security of the blockchain is increased when the Proof of Stake (PoS) works with the Proof of Work (PoW).
Under those implementations, miners produce blocks with the help of Proof of Work, and validators of PoS vote on the validity of those blocks.
The two projects working with HPoS are Decred and Hcash.
4- Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS)
With the inspiration of the Sequential Phragmen technique, Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) was launched in the late 19th century.
Nominated Proof of Stake(NPoS) selects validators to participate in the consensus method.
Being a variant of PoS, the NPoS is used in the substrate-based blockchain such as Polkadot, Edgeware, or Kusama.
Two actors who play significant roles in the NPoS are Validators and Nominators. Validators handle the work of infrastructure and network maintenance. Nominators or Token Holders select 16 validators of their choice and contribute to the network’s security.
Advantages of Proof of Stake
1- Saving of Energy
Proof of Stake saves energy because nodes are not competing for a block in the blockchain. Also, there is no requirement for mathematical computations under Proof of Stake, and thus, which saves energy.
2-Proper Validation
There are validator nodes under Proof of Stake (PoS) for validating blocks, whether they are accurate or inaccurate. Accurate blocks are given rewards, and there are penalties on inaccurate blocks where the owner loses specific stakes if approval is given for fraudulent transactions.
3-High Scalability
Proof of Stake is highly scalable in comparison to Proof of Work. As the Proof of Work is dependent on computation requirements, it becomes slower in processing transactions and thus, raising scalability issues.
But it’s not the case for Proof of Stake because it is decentralized and allows participation of individuals and groups, making it highly scalable.
Disadvantages of Proof of Stake
1-Accessibility Limitations
As the Proof of Stake requires staking the cryptocurrencies. Individuals can buy that specific PoS-based blockchain cryptocurrency through fiat money or exchange crypto coins from other platforms.
The higher the staking of the cryptocurrencies, the better chance to become chosen validator and earn the rewards. Thus, the individual needs to buy more cryptocurrencies to stake more and earn more.
The same situation exists under Proof of Work. If an individual or group of individuals holds money, he can buy highly computational equipment for mining and thus, increase his rewards.
2- The 51 Percent Attack
The Proof of Stake comes with the disadvantage as a 51 percent attack is a situation where an individual or groups of individuals can control the blockchain if they hold 51 percent of cryptocurrencies.
An individual or group of individuals in the PoS-based blockchain platforms can acquire an advantage against others in the new and low-valued cryptocurrencies. And this advantage can increase their chance of becoming selected validators.
Thus, an individual or group of individuals who have become chosen validators frequently will collect more transaction fees, increasing their stake and their chance of being chosen validators.
3-Relatively New Technology
Proof of Stake (PoS) has been around for a while, but it is comparatively new. It works a little differently than proof of work and has some advantages. Proof of stake can be more energy efficient and doesn’t require as much electricity to run. It is possible to create more coins/tokens with Proof of Stake (PoS) compared to Proof of Work (PoW).
Transitioning is the most considerable trouble from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). Moreover, Ethereum has announced its plan to switch to Proof of Stake. The transition is an ongoing process.
Ethereum’s mechanism is hindered by a slow transaction time, averaging 15 per second. And it doesn’t even scale.
Moreover, some people have another problem with rewards as they believe that the rewards from staking are less than those from mining.
The first cryptocurrency using Proof of Stake (PoS) was Peercoin which was introduced in 2012. Later, in 2017, a list of other cryptocurrencies using Proof of Stake was Nxt, Cardano, Blackcoin, and Algorand.
However, the most significant blockchain protocols currently using the Proof of Stake mechanism are Avalanche, Polkadot, and Solana.
Proof of Stake (PoS) in Ethereum
The transition in the Ethereum blockchain is happening through numerous upgrades to align Proof of Stake (PoS) as Ethereum 2.0. Beacon Chain, the first addition in the Ethereum 2.0 ecosystem, was added on 1st December 2020 and this brings staking to the Ethereum blockchain.
The users need to stake exactly 32 ethers to become a validator by registering contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. Validators order transactions and create new blocks where all nodes can agree on the Ethereum network. So far, there are more than 4,00,000 validators registered.
Mainnet, the current Proof of Work (PoW), will merge with the Beacon chain in phase 1.5 of Ethereum 2.0, “The Merge,” The tentative launch date is 19th September 2022.
You can check the deposit contract of the Beacon chain of Ethereum 2.0 here. If your stake is deposited once on the Beacon chain, then it can’t be turned back into Proof of Work (PoW) because there is no deregistration contract; there will be only validator-exit functionality where you can only withdraw ether to a shard in the Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain.
Functioning of Proof of Stake (PoS) in Ethereum
A randomizer known as RANDAO+Verifiable Delay Function (VDF) picks a registered validator on the beacon chain to create a committee. The registered validator is responsible for building the next block for a specific or two shards.
If a validator goes offline, they will lose their part of their stake periodically over time. The validator can also lose stake by performing a malicious activity like claiming a transaction is valid, which is not. The slashing of the stake is under the control of a mechanism known as a Slasher. And, if the validator has to withdraw the ether, a validator has to wait for several months.
The validator can propose a block only by combining the data from a specific shard with the Beacon chain data. Further, it stores attestations and lists of validators. Attestations are confirmed, and validators-signed hashes reflect the current state of a specific shard. If there is any change in the shard data, it is reported by the validators to the beacon chain. This helps shards to track each other’s changes with the help of a beacon chain which further enables the communication between them.
Conclusion
Adopting the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism to the blockchain has several advantages. The crucial point to ensure protocol safety is network synchrony. Even though numerous blockchains are actively using different variants of Proof of Stake (PoS), its real potential could only reflect with the upgrade of Ethereum 2.0.
About Zeeve
The leading blockchain infrastructure management platform, Zeeve, can deploy, monitor, and track nodes. We at Zeeve help build, deploy, and manage web3 infrastructure for enterprises and Blockchain startups. Zeeve is a platform that runs on low code web3 DevOps automation. As a team of experts, we are a one-stop solution for your blockchain solutions. Get in touch with our team to know more about blockchain solutions, node hosting services, and infrastructure management.