In the 21st century, the majority of industries are adopting blockchain technology. Whether it be healthcare, supply chain, finance, energy, media, logistics, power, and entertainment, every sector is harnessing the characteristics it possesses.
Blockchain technology is a distributed digital ledger that is maintained on nodes. Typically, a node acts as the backbone of a blockchain’s infrastructure that helps store, verify, broadcast, and distribute data to other nodes. Let’s quickly brush up on the concepts of nodes and learn in-depth what lightweight nodes are.
What is a blockchain node?
Nodes are an essential part of blockchain’s infrastructure that helps access information. Nodes are devices that work as a communication hub for various network tasks. The chief responsibility of a node is to confirm the legality of each subsequent batch of network transactions, known as blocks. A node ensures the data it holds is secure, valid, and accessible to the allowed people.
Simply put, a node is any system that connects to a network to perform specific duties across communication channels. The nodes operating within the network are interconnected and transfer all the information about transactions and new blocks. Also, it is easy to distinguish a node from other nodes by allocating a unique identifier to each node in the network.
Learning about different blockchain nodes is essential as most people confuse ‘node’ with a full node. However, they hold different meanings and seven types of nodes exist in the ecosystem. They are lightweight nodes, archival full nodes, lightning nodes, master nodes, pruned full nodes, authority nodes, and mining nodes. For this blog, we will keep our focus on lightweight nodes.
What is the purpose of running a blockchain node?
Nodes enhance security, maintain integrity, and provide credibility to the network. The node has unique features and helps to verify the network transactions. In short, nodes help provide trust and integrity to the blockchain and allow people to harness its true potential.
A network with more nodes helps instill a sense of reliability among stakeholders. It can be resilient to all kinds of attacks, hacks, and problems because of multiple blockchain nodes. You may need only one node to start a complete blockchain ledger to the new network.
What are lightweight nodes?
Lightweight nodes or Lightweight nodes are downloaded wallets connected to full nodes for validating the data stored on the blockchain. Simple Payment Verification (SPV) node or lightweight node is used in day-to-day crypto operations.
The contrasting difference is that they are smaller and only hold data about partial blockchain histories. Contrary, full nodes are a single copy of the blockchain history, including the timestamps, transactions, and all created blocks.
Lightweight nodes hold a block header instead of having a complete history of a blockchain. The header seeks to support and query the volatility of the previous transactions. A block header is the summary of a specific block that includes information related to the last block.
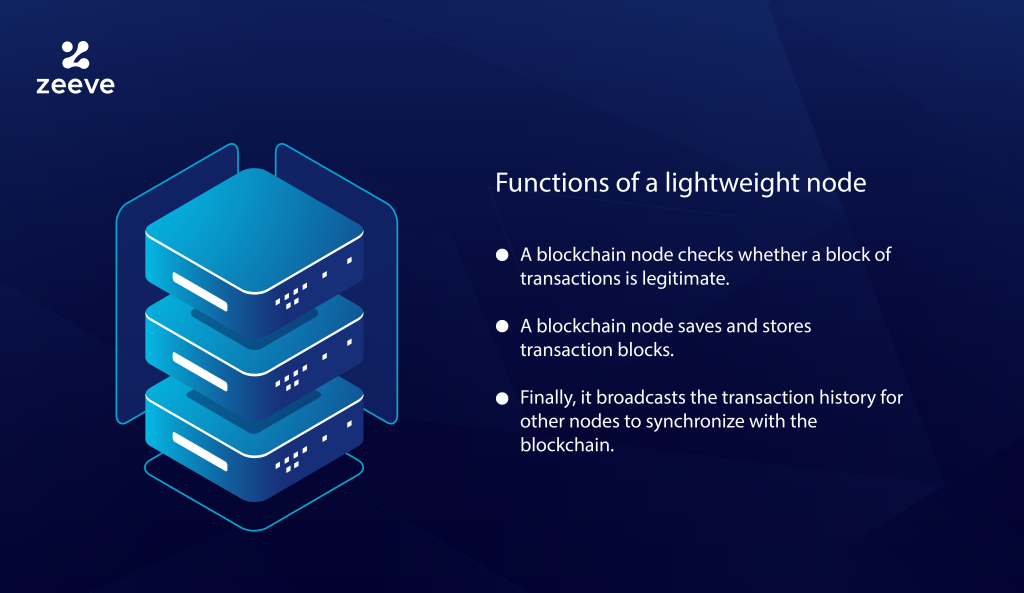
What are the functions of a lightweight node?
To understand the functioning of a lightweight node, let’s look over the complete process. In the background, a block broadcasts all the network nodes when the miner seeks to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. Depending on the legitimacy of a block, a node accepts or rejects the validity of signatures and transactions. Simply put, a node iterates the following steps:
- A blockchain node checks whether a block of transactions is legitimate.
- A blockchain node saves and stores transaction blocks.
- Finally, it broadcasts the transaction history for other nodes to synchronize with the blockchain.
How do blockchain lightweight nodes work?
Most of the current cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum, use a type of consensus algorithm known as Proof of Work (PoW). Although understanding the exact workings of PoW may be beyond the scope of this article, it’s main function is to prevent manipulation.
It uses a PoW algorithm, but it is shifting towards a PoS algorithm, which seems to be a more efficient way of preventing double-spends. Ethereum is currently using PoW as the main consensus algorithm, but it is gradually changing to a new algorithm known as Proof of Stake (PoS), which many consider a more efficient way of preventing double spending.
A consensus algorithm enables the nodes in peer-to-peer networks to effectively send, receive, and process data on the blocks of the blockchain and validate transactions.
How to Set Up a Lightweight Node
Learning to operate the full-scale node of any particular blockchain can be somewhat complicated for neophytes, especially with coding and specific crypto-related programs. The operation of a simpler tool such as lightweight nodes, however, can be easy to achieve by following a few simple steps. A lightweight node can be very easy to navigate by using a few easy steps.
To begin with, you must have a computer that meets the blockchain’s system requirements.
Unlike a lot of data, lightweight nodes are lightweight in terms of the data they consume. Often, lightweight nodes can be set up on devices like laptops and mobile phones, since such devices are often low in storage. Full nodes, however, have considerably more requirements, including varying settings, programs such as VPNs, security measures, and expensive hardware like mass storage devices.
Second, in order to put lightweight nodes on the Ethereum blockchain, you’ll need an application or software that can help you access the Ethereum blockchain. Programs and software used for this purpose are known as clients.
While running an Ethereum lightweight node, a client named Geth short for Go Ethereum will be needed. This client is coded in the Go programming language. Geth can be downloaded directly from the website. Using this tool will allow someone to join the Ethereum network through peer-to-peer transfer of Ether or being rewarded with cryptocurrency for performing mining.
What this node will do is store the Bitcoin blockchain header. A block header can be thought of as a fingerprint that is uniquely assigned to each block in order to distinguish it. Moreover, it’ll request any other desired information, such as data from the blockchain on demand. As of now, there are 10,500 active and reachable nodes within the Bitcoin blockchain.
Pros of using a lightweight node
The benefits of using a lightweight node are that they are convenient to use and it can be accessed with a couple clicks from a smartphone, computer, or other device. Lightweight nodes can be accessed via an internet connection using a smartphone or tablet anytime without the need for any awkward steps. This kind of wallet gives you access to your crypto assets at any time, from anywhere.
What are the potential risks (Disadvantages) of running a lightweight node?
A lightweight node comes with several risks if you plan to run it on the network. However, you can minimize the risks by configuring a node wallet to connect only to your full node.
Validation
The problem with lightweight wallets is that they do not validate the rules of bitcoin. For example, if somebody pays a lightweight wallet user with fake bitcoins, it will accept them, and the user has to bear the cost.
Security
Security is a significant concern among lightweight nodes as they skip several security steps making the user vulnerable. For example, an accidental chain fork on 4th July 2015 left all the lightweight nodes in danger while updated full node wallets were unaffected.
Privacy
The route of lightweight wallets involves sending addresses to a trusted third party and receiving wallet balance and history. It allows the trusted third party to spy on the user’s past and future transactions. However, full-node wallets download the entire blockchain and scan it locally to avoid this severe privacy leak.
Conclusion
Lightweight nodes or Lightweight nodes are downloaded wallets connected to full nodes for validating the data stored on the blockchain. It is essential to have knowledge of blockchain nodes and how it works. However, these expose you to security, privacy, and validation risks.
In recent years, some organizations are also offering node-as-a-service to help users skip running a node on their own. It is easy to integrate the node services even with a few clicks. A node service cuts down on the time you will spend maintaining and managing nodes by yourself. It lets you focus on the core work – building your product – rather than worrying about infrastructure maintenance.
Zevee will help manage and deploy your nodes
Zeeve is one of the leading blockchain infrastructure management platforms that supports businesses and start-ups to create, deploy, and manage decentralized applications and blockchain networks. Zeeve will ensure that your main focus lies in building the product while the team will take care of your needs.
The expert team has deployed over 2000 nodes and has proficiency in more than 15 blockchain protocols. Zeeve has a vast developer community with more than 45 blockchain experts that will handle some of the famous public and permissioned blockchain protocols. Get in touch with our team to learn about our blockchain sharing, managing, and deploying infrastructure platform.