Every business works with the goal of driving the growth of the company and bringing more revenue. But there are certain aspects that businesses are not able to handle. The “as-a-service” model targets both businesses and consumers. Further, it fills the organization with agility by catering to on-demand services.
Cloud services are booming and are projected to have a market value of $168.6 billion in 2024. Even the Blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) size will reach $11,519 million in 2026. Companies are nowadays focussing on the encryption of data along with hassle-free maintenance. This is possible mainly by opting for tailored as-a-service solutions.
Businesses mainly switch to “as-a-service” for two reasons either for infrastructure or application deployment. First, the services have been made possible by cloud computing. Although there are numerous models, a few of the major ones are — SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and BaaS. With the usage of the “as-a-service” model, you can focus more on the core services of your business.
In this detailed guide, you will read about blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) and other cloud computing services such as SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. We will also have a look at blockchain integration with IaaS, and PaaS.
“As a Service Model”
Cloud computing is defined as computing that, instead of having local servers, relies on on-demand computing resources. As a result, cloud services reduce upfront IT costs & also eliminate the need to maintain local infrastructure.
Cloud computing is the foundation of as-a-service models. However, the model’s popularity also increased after the emergence of — IoT and edge computing. The services are majorly used by enterprises and are also preferred by individuals.
The services act as an endpoint to the final application. The users access the services via a web browser. For example, Gmail is a SaaS application that many of us operate through the browser. Now let’s understand more about the services.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is also known as web-based software, hosted software, or on-demand software. Everything on SaaS is managed on the cloud. Software as a service can be accessed via the Internet, and there is no hardware management here. Therefore, instead of installing the software, you access it through the Internet.
SaaS has a multitenant architecture which means all users share the common infrastructure. The code base for the users also remains the same. It updates the traditional business process by point-and-click. Many organizations are also providing SIPs or SaaS integration platforms. As CRM software isn’t affordable for small businesses, SaaS offers better access and management of data from a networked device.
The cloud provider gives the complete software, for example — application codes, databases, server, etc., in the form of service. The service is on-demand software for the users and is licensed and later delivered to the users.
Advantages of SaaS
- On-demand service: There is no high capital expenditure required you can just pay and get an on-demand service.
- Self-Updated: There is no need to update the SaaS software as it works on the cloud; it gets updated itself to the latest version.
- Easily Accessible: The services are easy to access and can be availed through any networked device.
- Scalable: More people in an organization can use the system, and the services can adapt volumes of data efficiently.
- Easy migration to hybrid model: Development options are available for hybrid devices such as mobile, computers, and cross-platform apps.
Disadvantages of SaaS
- Limited Customization: Often, the software is incompatible with the existing hardware thus making less room for customization.
- Security concerns: The security is handled by the SaaS company. Thus, any leak of data can place your company at risk.
- Fewer Features: The SaaS apps are standardized and thus there isn’t an option to customize the app. The solutions also have more latency compared to server apps making it slow.
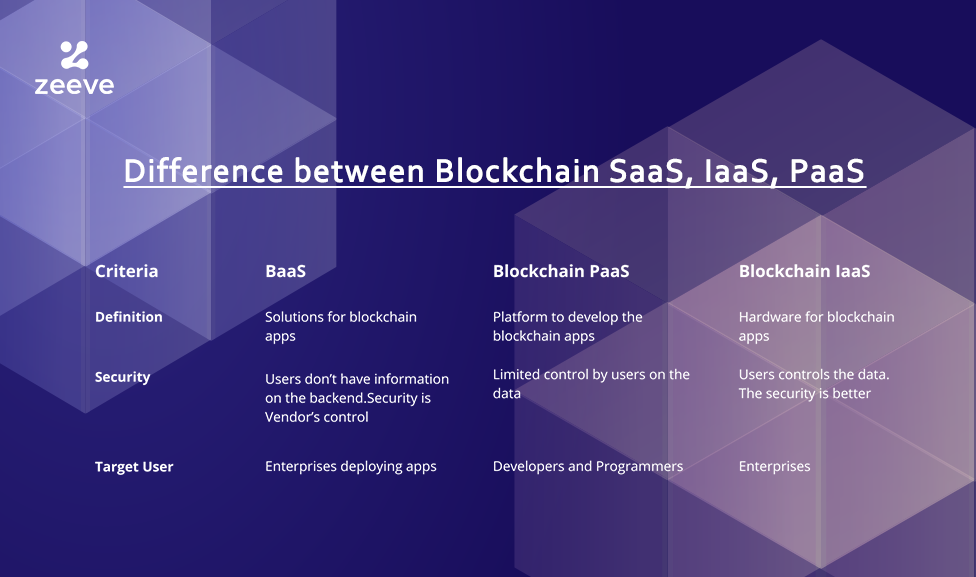
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)
BaaS manages the cloud-based networks for businesses that work for blockchain-based applications. You may understand BaaS as similar to SaaS, where we can operate, build and host apps.
A service provider handles the backend operation bandwidth management, hosting, and data security. Cloud services are essential for the operating, hosting, and developing of blockchain-based applications.
The BaaS service provider is responsible for maintaining blockchain-related fragments and the infrastructure. The blockchain network can also be selected as per the requirements such as — Bitcoin, Ethereum, Hyperledger, Corda, and many more.
Read: Discover Everything you Need to Understand BaaS — The Quintessential Beginner’s Guide to BaaS (Blockchain as a Service)
Is Blockchain as a Service similar to Backend as a Service?
Blockchain as a service (BaaS) should not be confused with backend-as-a-service. Although blockchain provides customized business logic along with APIs so it is close to the definition of the backend. However, blockchain also carries the frontend features such as running, distributing, and scaling. Therefore, blockchain functionality lies in between the backend and frontend.
Advantages of Blockchain-as-a-Service
- Trustlessness: The term trustless means that we don’t need to trust any bank or any intermediary to avail transactions.
- Immutability: The transactions on the network are immutable along with time & date stamps. Therefore, any information once uploaded, cannot be tampered with.
- Traceability: An audit trail is present on the blockchain network which makes it easy to secure to trace the weaknesses in any network.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are the feature that speeds up the transaction process once the pre-specified conditions are met. This feature makes less interference from third parties.
Disadvantages of Blockchain-as-a-Service
- 51% attacks: The consensus algorithm is said to be secure. Nonetheless, attacks may occur if the attacker is able to control half of the network’s hashing power also known as 51% attacks.
- No modification: One has to be very careful while uploading any kind of data as changing any pre-existing data requires a hard fork.
- Store Private Key: It’s the user’s sole responsibility to keep the private key safe, as once lost, the user will not be able to retrieve their assets.
Read: Want to understand in detail about Blockchain-as-a-Service? — Read one of our blogs here
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a service provides cloud components for certain software. It further provides a framework for building the customized application. In SaaS, we deliver the software over the internet while here, the aim is to provide the platform to the developers for software creation.
PaaS is mainly about cloud computing, where we manage the applications and data; rest all the runtime, middleware, O/S, etc., are managed on the cloud.
The platform (runtime) service is initially sent on the web; the developer has the freedom to build the software without thinking much about the operating systems, infrastructure, storage, and software updates. To deploy PaaS, the developers can choose — Public, Private and Hybrid solutions.
Read: Discover How Rollups-as-a-Service can Transform your Blockchain Strategy — A Deep Dive into Rollups-as-a-service (RaaS)
Advantages of PaaS
- Cut coding time: With the availability of pre-coded applications and the workflow, directory services, etc. the amount of coding work is reduced by using PaaS.
- Easily available: It allows you to log in and operate the applications from anywhere.
- Scalable: PaaS offers dynamic scalability by rapidly adding capacity in peak times and also provides the option of scaling down.
- Developers have the choice to customize: Range of operational tools so developers can create customized software.
Limitations of Using PaaS
- Vendor Lock-in: There are some features that are not for the user. Such features are locked-in. In that case, users have no choice left.
- Compatibility: The components in PaaS are not always cloud-enabled, and thus because of its infrastructure, the platform may face compatibility-related issues.
- Reliability concerns: On the PaaS one can face challenges related to frequent downtimes. The users should create backups to avoid any loss of data.
- Lack of control: The users have less control over the pricing of PaaS solutions. The provider can sometimes increase the pricing scheme.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
By deploying IaaS, you can purchase, install, configure and manage your software, operating systems, middleware, and applications. The goal is to provide infrastructure to online businesses.
On IaaS, the applications, data, runtime, middleware, and O/S are managed by you. On the other hand, visualization, servers, storage, and networking are managed on the cloud. IaaS is one of the types of cloud computing which offers storage and networking resources on demand.
For the IaaS, you have to pay-as-you-go basis, which means you pay as long as you require the service. The physical servers and data centre infrastructure are replaced with cloud infrastructure. Furthermore, there is a cloud computing service provider which manages the infrastructure.
Read: Ready to Launch your Blockchain? — Start Deploying your Custom Network Today!
Advantages of Using IaaS
- Faster innovation of apps: The computing infrastructure is ready in hours rather than in weeks, thus quicker delivery to users.
- Less capital expenditure: The maintenance & hardware costs are reduced as the configuring and managing of a physical data centre is migrated to the cloud.
- Experimental: Perfect for temporary or can be used on an experimental basis. Once the new software is tested and refined, the business can be moved to traditional, in-house deployment.
- On-demand scaling: With IaaS, it’s easy to increase and decrease the data storage. One gets the option to pay for the additional services.
- No physical server required: By using IaaS, you don’t require any physical server to maintain the infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Using IaaS
- Unexpected Costs: Close monitoring of bills has to be done in the pay-as-you-go billing process. Suppose the usage of the platform increases, the bills will increase as well.
- Third-party service: The services are top-notch still, the major issue is that it is a third-party service provider. For instance, AWS owns the hardware, and therefore, they handle all the computing resources.
- Security: A common misbelief that the infrastructure is provided by other providers thus data is completely safe; this is true to some extent, but as a user, ultimately you are in charge of the data.
Blockchain Integration with two different Services
Here are the two types of integration of the blockchain technology with other as-a-service models:
- Blockchain IaaS: The blockchain can be delivered as an IaaS model with on-demand infrastructure. The companies get provisioned on-premises computing. Organizations get the benefit of using the functionalities of blockchain along with cloud providers.
- Blockchain PaaS: Again, similar to IaaS, the blockchain PaaS provides a platform for the management of blockchain infrastructure. The service also does not require any installation procedures. Though, the service involves customization to align the systems together.
Summing it all up
These are a few of the cloud service models that you may witness in the world of cloud solutions. You can try any of these cloud service providers depending on the requirements.
The solutions enable a dynamic business model by breaking down innovation barriers by providing analytics and reducing expensive capital investment. Over the few years, more and more organizations are opting for the above-mentioned service models and experimenting with hybrid environments.
With the experience of working with industries across the globe, Zeeve will help you deploy a cloud infrastructure per your requirements.
Partner With Zeeve
Zeeve is a low-code automation platform that supports the backends of several blockchain protocols and other cloud services. It not only deploys and builds the blockchain networks but also supervises their nodes.
Get in touch with our team to learn about our blockchain sharing, managing, and deploying infrastructure platform.